The debate surrounding physical borders has been a pivotal aspect of world politics and history. Focusing on the US-Mexico border wall, this essay will unpack an array of layers surrounding this contentious issue. An effort will be made to pore over the historical context of border creation, delve into the implications on socio-cultural fabric, comprehend the ever-changing political dynamics and inspect the economic aspects connected to this monumental construction. Furthermore, the essay will shed light on the ecological effects stemming from this significant interjection within diverse ecosystems.
Table of Contents
Historical Context of Borders
Bearing witness to the significant role of history in shaping society, the concept of the US-Mexico border wall doesn’t escape this influence. This article delves into the historical matrix that has fostered the idea of the border wall, informing its present discourse.
The United States-Mexico border has had a mutable significance over time, shifting in accordance with the socio-political climate. An intriguing component of this is the unalterable geographic co-location of the two nations. Indeed, as the saying goes, “You can’t choose your family, or your neighbors.”
With a constant proximity of 1954 miles, the shared border has been instrumental in establishing both harmonious relations and discord. The demarcation of the border began post the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo in 1848, which ended the US-Mexico war and expanded US territories. However, the idea of a solid physical barrier thereafter was non-prevalent for over a century, symbolizing a permeable, interactive interface.
An initial spurt in the border-security focus can be linked back to the era of ‘Prohibition’ in the 1920s. The increased illegal cross-border flow of alcohol and, later, narcotics, fostered the induction of a border patrol force in 1924. However, a permanent physical barrier was absent even then.
It wasn’t until the 1990s, under the administration of Bill Clinton, that the narrative began to pivot towards significant physical barriers, correlated with debates over Free Trade Agreement and seen as an attempt to control illegal immigration. To note, ‘Operation Gatekeeper’, deployed physical barriers along the most trafficked border区域, yet, the idea of an all-encompassing wall was still not there.
The border wall idea, as it stands today, was strategically brought into limelight during the Donald Trump presidential campaign in 2016, and has since remained a hot-button issue. The ‘wall’ sentiment taps into deeper socio-political chasms dating back to America’s roots — issues relating to immigration, national identity, cultural preservation, and economic disparities.
Yet, it remains important to consider that this decision does not exist in a vacuum. It is a testament to the evolution of policies, intertwined with the historical context and cultural identities. Also, it is significant to understand, in addressing these complex issues, that a physical wall cannot simply rectify them.
In sum, the historical context carries significant weight in shaping the border wall idea. It echoes the changing scenario of shared socio-political dynamics, reflecting on the continuity of interactions between the two nations. The full understanding of these dynamics forms an enriching context that bolsters comprehensive deliberation on the subject.

Sociological Implications
The sociological implications of the US-Mexico border wall extend far beyond its role as a physical deterrent to illegal immigration. The notion of constructing a formidable barrier assumes a multi-faceted significance, influencing political, cultural, and social aspects of both nations.
To consider the political repercussions, the border wall has transformed into a symbol for broader controversies involving policy-making and national security. Conversely, it has also been criticized for diverting attention from other critical issues such as healthcare, education, and economic inequality. The decision to construct the wall was accompanied by significant political polarization, serving to widen existing ideological divides rather than enhancing national cohesion.
From a cultural standpoint, the wall threatens to disrupt the rich blending of Mexican and American cultures that has occurred over centuries along the border regions. The implicit message seems to be one of cultural disassociation, rather than mutual respect and understanding. This side-effect of building the border wall could engender an atmosphere of cultural intolerance and xenophobia, which in turn could greatly affect the social dynamics within the local and even national communities.
Socially, the border wall creates an insurmountable barrier to the traditional human interactions that transcend geopolitical boundaries. Instead of a multicultural space that fosters interactions, the border region risks transforming into a no-man’s land heavily policed and monitored. This redefinition of the spatial dynamics could potentially reduce interpersonal exchanges, create an atmosphere of distrust, and exacerbate socio-cultural divides. Further, it has potential to normalize the viewpoint of hostility towards the ‘other’, specifically marginalized and disenfranchised groups.
Moreover, the wall has the potential to confer negative perceptions of immigrants, particularly those from Mexico and other Latin American countries, making their assimilation into American society even more challenging. With the rhetoric associated with the establishment of the border wall, these communities could become further marginalized, exacerbating racial and class divides.
Conclusively, the decision to construct a physical border wall between the United States and Mexico has far-reaching sociological implications. While serving as a geographical boundary, it also manifests itself as a political symbol, a cultural divide, and a social barrier. As geographically adjacent nations, their shared history, interconnected economies, and co-existent communities continue to shape their relations. The border wall, intended or not, casts a shadow on these intricacies, complicating a socio-political landscape that extends far beyond the miles of concrete and steel. The full impact of these sociological implications remains to be seen, noted, and potentially mitigated. Therefore, the border wall is not just a concept or a construction project, but a long-lasting mark on the socio-cultural landscape of two nations.

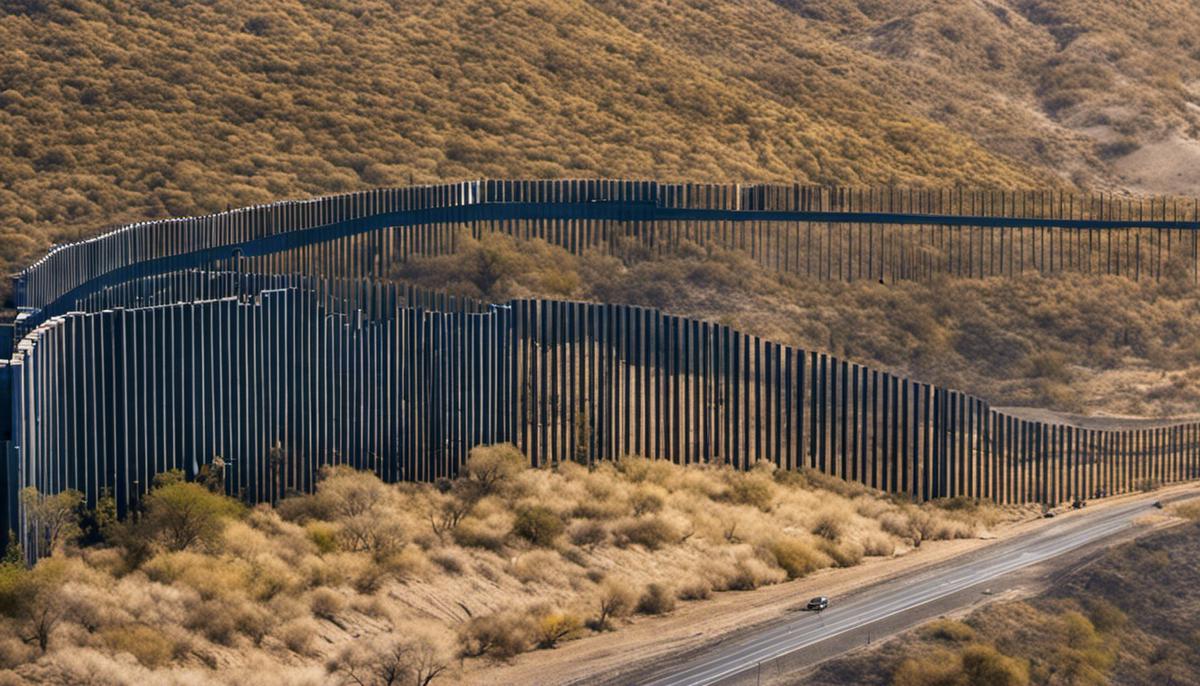
Political Dynamics
Moving on from historical scrutiny, the construction of the US-Mexico border wall is not merely an ambitious infrastructure project, but a catalyst for significant political repercussions. Some critics argue that the focus on the border wall has drawn attention away from other core policy issues, such as healthcare, climate change, and national debt – the contention is that resources spent on the wall might be redirected toward tackling these challenges instead.
Given the polarizing nature of the border wall concept, it has further widened ideological divides among the American public. It casts a potent spotlight on the political landscape, where support or opposition for the wall typically splits along party lines. This polarization extends beyond politics to permeate social interactions and communal exchanges.
Unquestionably, one of the most profound impacts of the border wall involves cultural dynamics. The close proximity of the United States and Mexico has facilitated a rich amalgamation of their cultures over centuries. The border wall is perceived by some as a threat to this cultural fusion, fostering cultural disassociation and, in the extreme, xenophobia. This outlook inadvertently harms the societal fabric, hampering interpersonal exchanges between different communities and fragmenting the multicultural mosaic that defines the region.
Further, the border wall fosters an atmosphere of distrust and heightens socio-cultural divides. It fortifies negative stereotypes associated with immigrants, particularly those entering the United States from Mexico and Central America, thereby exacerbating challenges associated with assimilation. As such, the wall may deepen the rift between communities, creating a confrontational rather than collaborative environment.
Most distressingly, the border wall’s implications extend to its impact on marginalized and disenfranchised groups. Those seeking asylum or migration for a better life often find themselves caught in the crossfire of this issue, their plights overshadowed by political rhetoric and polemics.
In sum, the US-Mexico border wall has far-reaching socio-cultural implications that echo across the landscape of US-Mexico relations, casting a long shadow over the complexities of these interactions. It is far more than a physical divider, acting as a flashpoint in heated debates on sovereignty, identity, and humanity. Regardless of its physical manifestation, the border wall embodies the intensifying pulse of a relationship between neighbors, the dynamics of which reverberate within and beyond their territories.

Economic Considerations
Analyzing the economic implications associated with the United States-Mexico border wall is an exercise steeped in complexity. It requires deep understanding of the intertwined economies of these nations, demography, migration patterns, labor markets, and the intricacies of international trade. It further demands an acknowledgement of the border’s role not only as a liminal locale, but also as a bustling hub of economic activity.
First in these considerations is the considerable expenditure associated with erecting such a physical structure. Various estimates range from $15 billion to $25 billion for constructing the wall. The cost burden, whether sourced from taxation or redirection of public funds, indeed poses economic impacts for American citizens. Adding up to this are the maintenance cost, land acquisition, environmental implications, and the cost of potential litigation involved.
An integral component of this dialogue concerns trade. The economic intertwining of the United States and Mexico are pronounced, with Mexico being the United States’ third-largest goods trading partner, and second-largest goods export market in 2019. Goods trades have quadrupled since 1994, reaching an estimated $614.5 billion in total (two-way) goods trade during 2019, adding substance to the argument that any impediment to this interaction may have reverberating impacts on the American economy.
Equally important is the domino effect the wall may impose on labor market dynamics. Mexico’s 2012 net migration rate is marked as the second most significant contribution to U.S. civilian labor force growth. The U.S. civilian labor force would increase by approximately 6.4 million from 2012 to 2022, with net international migration expected to account for 62.5 percent of this increase. It is thereby crucial to examine how an augmented border wall might affect these trends.
A discourse on the border wall’s economic implications would not be complete without addressing the dynamics of illegal drug trade. Transnational criminal organizations operate across the U.S.-Mexico border and generate billions of dollars in profit from drug trafficking. By creating a physical barrier, these illicit activities might be curtailed; however, the promise of impenetrability and the subsequent reduction of drug flow remains debatable. Conversely, an enhanced border wall could potentially escalate drug prices due to increased risk and operational cost, inadvertently enriching the cartels further.
Last but not least, the tourism and remittances from the United States to Mexico, which amounted to more than $30 billion in 2017, may undergo dynamic changes. A fortified wall could impact tourism from both sides by fostering negative sentiments and perceived hostility.
In conclusion, it is important to move past simplistic binary narratives and delve deeper into the labyrinthine discourse surrounding the U.S.-Mexico border wall. The ability of a physical barrier to address and potentially remedy socio-economic issues is questionable as these challenges demand solutions far more intricate than concrete and steel. It is thereby essential to foster a comprehensive understanding that considers the dynamic, interlocked, and multidimensional nature of the economies and cultures which traverse this border. This necessitates that the discourse on the border wall be analyzed within this more extensive, intersecting, and interdependent framework. In doing so, it becomes increasingly apparent that the economic implications are multifaceted, broad, and far-reaching. The border isn’t just a boundary but a complex hive of economic, cultural, and social interactions.
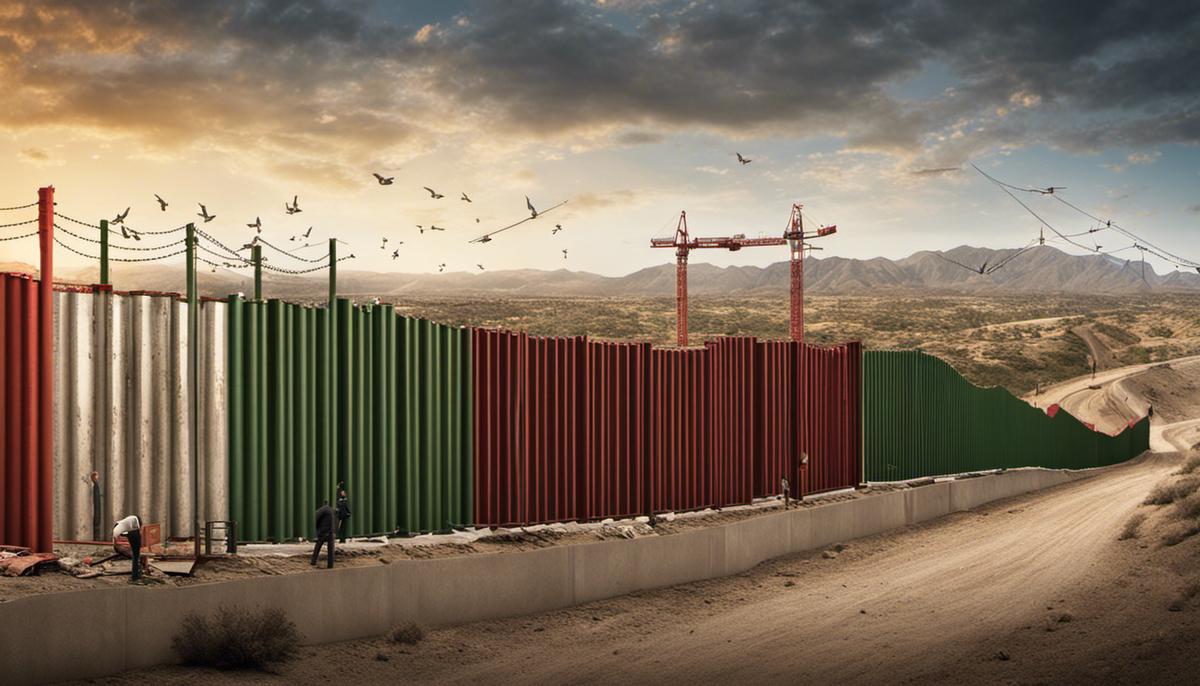

Environmental Impact
Navigating the Environmental Impact of the US-Mexico Border Wall
With policy discussions, socio-political discourses, and explorations of the cultural and economic implications of the US-Mexico border wall, one spectrum of impact remains largely uncharted — the environmental front. This article shines light on this aspect, dissecting the environmental implications of the physical wall, motivated by a firm dedication to enhance the collective understanding of the ripple effects of such a gargantuan man-made structure.
To begin this discourse, the geographical milieu must be understood. The US-Mexico border traverses through an expansive array of ecosystems encompassing various landscapes – deserts, mountains, rivers, and wetlands to name a few. Each of these ecosystems, a unique tapestry of biodiversity, hinges on the parennial flow of species, nutrients, and water across the border.
The border wall, by virtue of its physicality, obstructs this flow. The implications of the resulting fragmentation of ecosystems can be far-reaching, leading to plummeting biodiversity levels and unsupportable shifts in the population dynamics of flora and fauna alike. Organisms dependent on cross-border movement for migration, foraging, or mating may face survival challenges with detrimental consequences rippling across the food web.
Beyond affecting terrestrial life, the wall holds significant repercussions for water systems as well. Crucially positioned riparian habitats – breeding grounds for a wealth of avian, mammalian, and aquatic species – may be disrupted. The wall may also obstruct water flow, aggravating flooding in heavy rain seasons and impacting the water table. Moreover, water scarcity issues may be exacerbated as the wall disrupts the patterns of surface water flow in regions like the Colorado River delta and Rio Grande.
Then there’s the dark specter of climate change. With climate-induced pressures reshaping habitats, animals seek new territories for survival. The wall could imperil this essential climate adaptation strategy, leading species towards localized extinction.
Furthermore, the construction process itself poses severe environmental costs, including rampant deforestation, habitat destruction, alteration of the landscape, and runaway carbon emissions from material extraction, processing, transportation, and construction.
Finally, an informed discourse warrants a discussion on the wall’s potential impact on protected habitats. Numerous protected areas and wildlife reserves, including the Sonoran Desert National Monument, San Bernardino National Wildlife Refuge, Cabeza Prieta National Wildlife Refuge, and Lower Rio Grande Valley National Wildlife Refuge overlap with the proposed border wall route. This monumental project threatens the very sanctity of these havens of biodiversity.
To conclude, the environmental implications of the US-Mexico border wall cannot be marginalized. It’s imperative that these considerations echo in policy discourses, stirring a collective acknowledgment of the ecological costs of such endeavors. For in the canvas of nature, there aren’t borders, just a seamless tapestry of life – an interconnected play of species, elements, and ecosystems. A wall, after all, holds consequences stretching beyond human realms.

This concise exploration of the US-Mexico Border wall as a historical, socio-cultural, political, economic, and ecological phenomenon, suggests that its implications are far-reaching. It has tangibly altered political dialogues, influenced cultural assimilations and antagonisms, reshaped economies and left an indelible impact on local environmental systems. Moreover, it symbolizes profound global questions concerning national identity, security, immigration and the intersection of human constructs with nature. Recognizing and understanding its multifaceted nature are crucial steps towards productive debates and informed policy decisions concerning borders and migration.

Matt Smith is a seasoned journalist and author whose expertise spans across the dynamic realms of Politics, Gadgets, Gaming, and a plethora of general interest topics. With a Master’s in Political science and tech pedigree shaped in Silicon Valley, Matt brings a wealth of knowledge and a critical eye to everything he writes.
Politics: Matt offers sharp political commentary, drawing from his experience as a political analyst and his academic rigor.
Gadgets: His tech insights are grounded in real-world experience, having been on the front lines of innovation with a degree from Caltech.
Gaming: A respected voice in gaming, Matt’s reviews and trend analyses are a testament to his deep involvement in the gaming community.
General Topics: From science to culture, Matt’s writing spans a broad spectrum, engaging readers with a blend of expertise and relatable prose.
Engage with Matt’s compelling content for a fresh perspective on the issues at the forefront of today’s discourse.